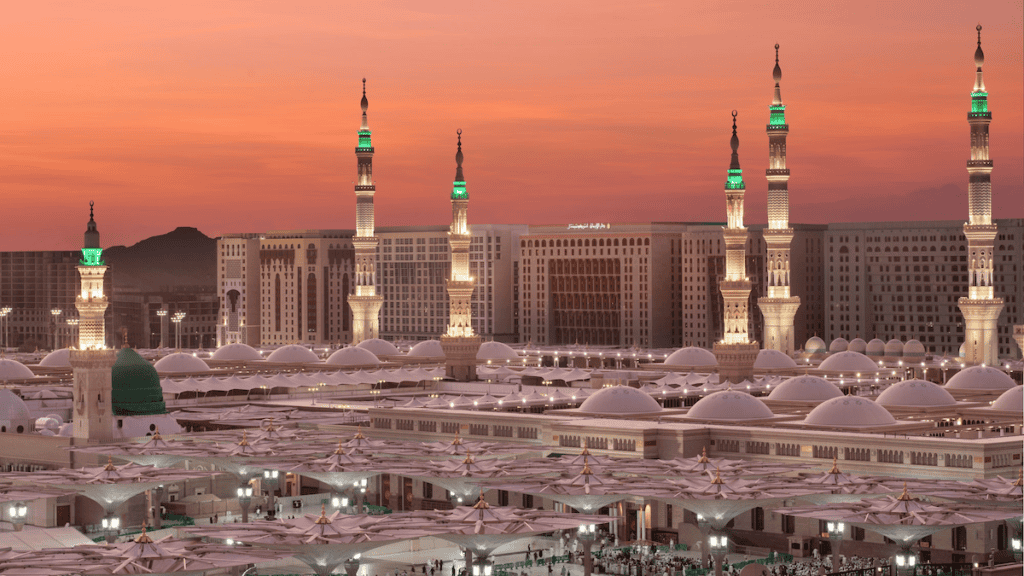
Have you ever yearned for a place you’ve never been, felt a connection to a city you’ve never seen?
That’s how I feel about Madinah.
It’s not just a city on a map; it’s a holy city where the air feels blessed.
Madinah is where our beloved Prophet Muhammad (Peace be upon him) found a home after facing hardship in Mecca.
He built his mosque, the Prophet’s Mosque, which still stands at the city’s heart.
Madinah is the second holiest city in Islam because it’s where our Prophet (Peace be upon him) rests, along with some of his closest companions in the cemetery of Al-Baqi.
For Muslims, Madinah is a place of deep spiritual longing. Every year, millions of us pilgrimage to walk in the Prophet’s footsteps.
It also holds the Quba Mosque, the very first mosque in Islam. That’s why only Muslims are allowed to enter Madinah – it’s a place dedicated to our faith.
Madinah is a city that has grown and changed over time, yet the spirit of Islam remains its foundation.
Its economy focuses on serving pilgrims, and reverence for this holy site is a part of every aspect of the city.
Madinah Through the Ages
Yathrib: Madinah’s Roots
Before it was the City of the Prophet, Madinah was called Yathrib.
It was a bustling oasis town where people grew dates and traded goods. Different tribes lived there, including some Jewish groups, and they shared a rich history.
A City Yearning for Change
While Yathrib was prosperous, arguments and disagreements between tribes made life difficult.
Meanwhile, in the nearby city of Makkah, the Prophet Muhammad (Peace be upon him) was sharing the message of Islam.
His teachings challenged the way many in Makkah lived, causing problems for him and his followers.
The people of Yathrib heard about the Prophet (Peace be upon him) and his call for peace and justice.
Secretly, a group of them pledged their allegiance to Islam and invited him to their city.

The Hijra: A New Beginning
The Prophet Muhammad’s (Peace be upon him) journey from Makkah to Yathrib is known as the Hijra, a pivotal moment in Islamic history.
Madinah welcomed the Prophet (Peace be upon him) with open arms, becoming a place where Muslims could live in peace. It was renamed “Al-Madinah al-Munawwarah,” meaning “The Radiant City.”
Madinah’s Transformation
Over the years, Madinah went through many changes:
- Building a Community: Under the Prophet’s (Peace be upon him) guidance, Madinah became a model Islamic society. The first mosque (Quba), Masjid al-Nabawi (the Prophet’s Mosque), was built as the community’s center along with other mosque.
- Challenges & Growth: Medina faced battles and hardships, but it continued to grow and become a major center for Islamic learning. We remember these stories as testaments to our faith.
- Ottoman Rule: For centuries, Madinah was part of the Ottoman Empire. They expanded the holy sites, leaving a beautiful mark on the city.
- Saudi Era: Madinah became part of Saudi Arabia in the early 1900s. Today, the Saudi government cares for the holy sites and manages Madinah’s development.
- Modern Developments: Madinah is now a modern city with an airport, high-speed railway, and services for the many pilgrims who arrive all year round. Its economy heavily relies on serving those who come to connect with their faith.
The City of Light – Madinah’s Transformation
A Community Built on Faith
The arrival of the Prophet Muhammad (Peace be upon him) transformed Madinah.
One of his first acts was building Masjid al-Nabawi (the Prophet’s Mosque).
It was more than just a place of prayer, it was the beating heart of the new Muslim community.
Here, people from all backgrounds gathered to worship, learn, and find a sense of belonging.

A City of Justice and Compassion
The Prophet (Peace be upon him) created a society built on fairness, kindness, and helping those in need.
Laws were made to protect everyone, no matter their tribe or wealth.
This sense of justice is something so important in Islam, and Madinah became its shining example.
Challenges and Strength
Of course, life wasn’t always easy in Madinah.
Enemies attempted to attack the city, and there were times of hardship.
But through it all, the Prophet Muhammad (Peace be upon him) led by example.
He taught us bravery, patience, and most of all, unwavering faith in Allah.
The Radiant City
Madinah isn’t called the Radiant City just because it’s beautiful.
It’s filled with the light of faith.
Islam teaches us that Allah blesses Madinah, keeping it safe and rewarding those who pray or give charity here.
It’s said that angels protect the city, and it will remain a beacon of hope, even during difficult times in the world.
Madinah’s Influence
Madinah was Islam’s first capital, and it became a model for other Muslim cities across the world. Here’s why:
- Focus on Community: Helping each other, regardless of our differences.
- Importance of Education: Madinah became a center of Islamic learning and knowledge.
- Fairness and Justice: Laws and systems that treated everyone equally.
The impact of Madinah can be felt throughout Islamic history and continues to inspire Muslims everywhere.
Sites of Significance in Madinah
Madinah is filled with places that hold deep meaning for Muslims. Let’s explore a few of the most important:
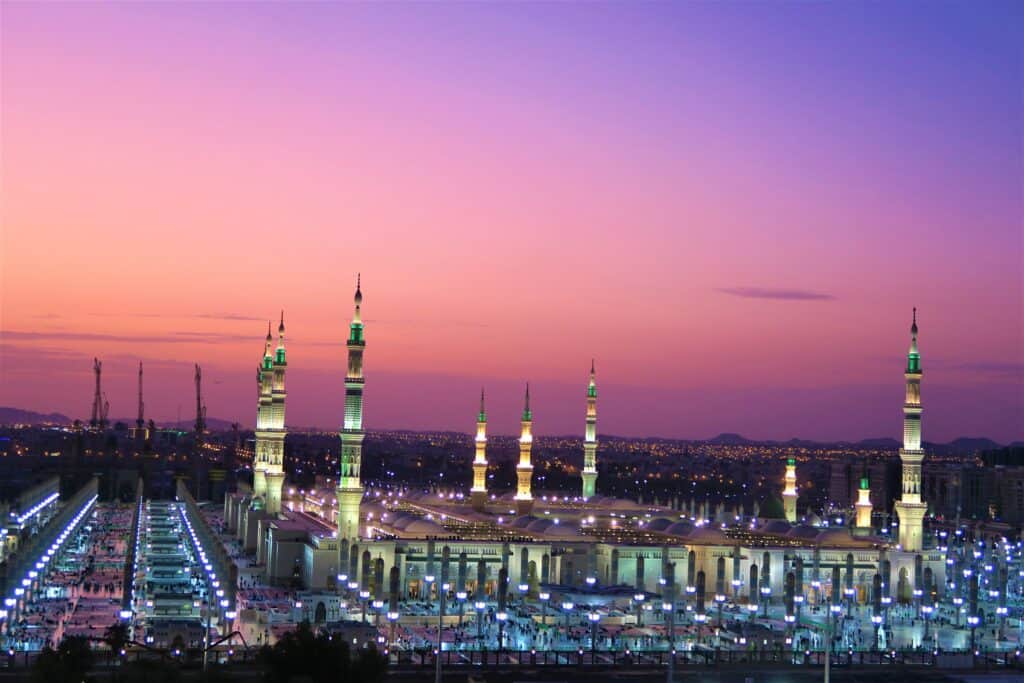
Masjid al-Nabawi (The Prophet’s Mosque)
This is the heart of Madinah. It was built by the Prophet Muhammad (Peace be upon him) himself and has been expanded many times throughout history.
At its center is the Green Dome, which marks the Prophet’s (Peace be upon him) resting place.
Muslims from all over the world dream of praying in this mosque – the rewards are believed to be immense.
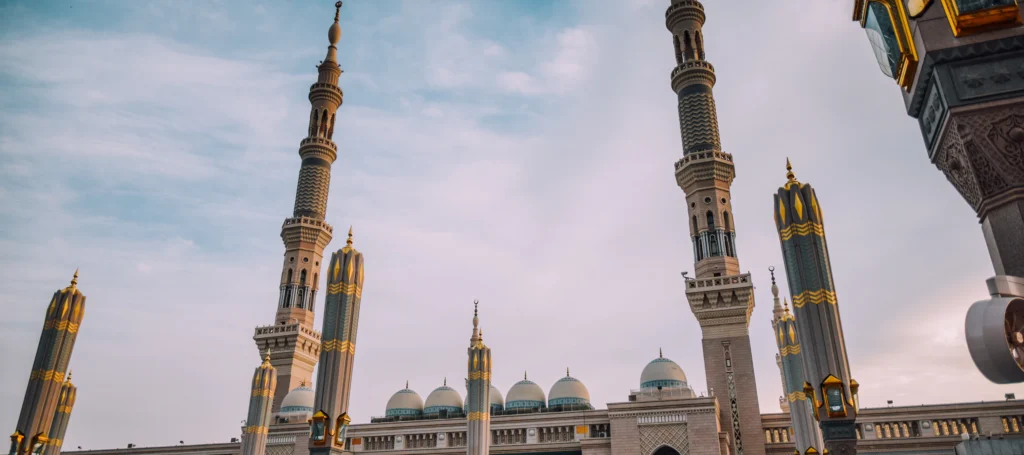

Quba Mosque
This mosque is especially significant as the very first mosque built in Islam.
It’s where the Prophet Muhammad (Peace be upon him) and his companions stayed upon arriving in Madinah from Makkah. Performing prayers at Quba Mosque is a great reward for Muslims.
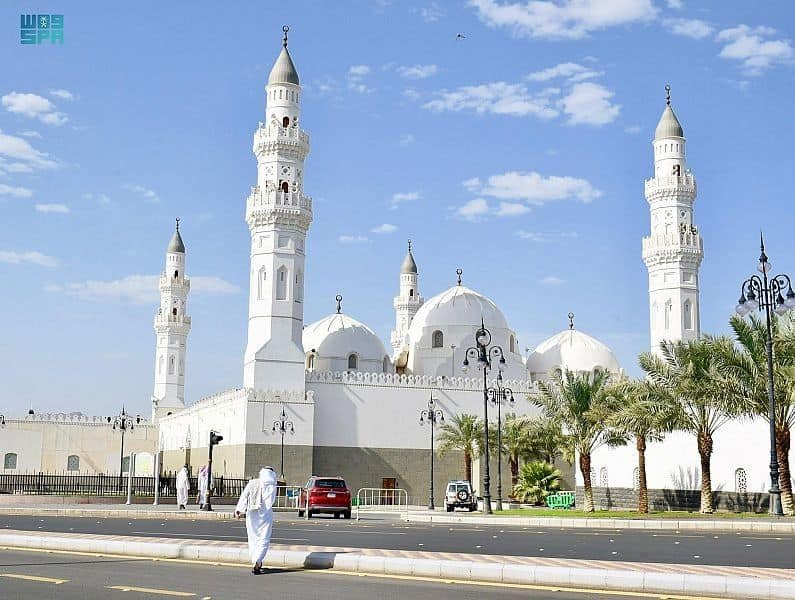

Al-Baqi Cemetery
This cemetery is just outside the Prophet’s Mosque. It’s where many of the Prophet’s (Peace be upon him) family members and closest companions are buried. Visiting Al-Baqi is a way to pay respect and remember those who played such an important role in early Islam.

Other Key Sites
- Masjid al-Qiblatain (Mosque of the Two Qiblas): This mosque is special because it’s where the direction of prayer (qibla) changed from Jerusalem to Makkah.
- The Seven Mosques: These small mosques mark the site of a historical battle, reminding us of Madinah’s struggles and triumphs.
- Mount Uhud: This mountain was the site of another important battle in early Islamic history. Visiting Uhud is a way to reflect on sacrifice and resilience.
The Essence of Madinah
These are just a few of the many sacred places in Madinah. Every corner of the city feels filled with history and the presence of the Prophet (Peace be upon him). It’s a place to connect with the roots of Islam and feel the power of faith.
Visiting Madinah – A Pilgrim’s Guide
The Journey of Hajj and Umrah
Millions of Muslims each year make the incredible journey to perform Hajj or Umrah.
Hajj is one of the five pillars of Islam, a pilgrimage to Makkah that every able-bodied Muslim aims to complete at least once.
Umrah is a shorter pilgrimage, also to Makkah, that can be done at any time of year. Many pilgrims choose to include a visit to Madinah on their sacred journey.
The Madinah Experience
Visiting Madinah is an experience like no other. Here are some of the things you might feel and do as a pilgrim:
- Spiritual Connection: Praying in Masjid al-Nabawi, standing close to the Prophet’s (Peace be upon him) resting place, and feeling the energy of this holy city – it can awaken a deep sense of peace and closeness to Allah.
- Reflection and Remembrance: Visiting Al-Baqi, Uhud, and other historic sites allows you to honor the Prophet’s companions and learn from their stories.
- A Sense of Community: Being surrounded by so many Muslims from all over the world strengthens the feeling of brotherhood and sisterhood central to Islam.
Practical Tips
- Timing your Visit: Madinah can be very crowded, especially during Ramadan and Hajj season. Consider a less busy time if you want a more peaceful experience.
- Logistics: You’ll need a visa if you’re not a Saudi citizen. Arrange your transport and accommodation well ahead of time.
- Customs and Etiquette: Dress modestly, learn some basic Arabic phrases, and be respectful of local customs.
More Than a Trip
Visiting Madinah isn’t just about ticking off a checklist of sites. It’s a chance to renew your faith, connect with fellow Muslims, and hopefully come home with a deeper understanding of Islam’s history and spirit.
Madinah’s Legacy in the Modern World
Madinah isn’t just a city frozen in time. It’s a place that continues to shape the Muslim world today.
A Center of Islamic Knowledge
Madinah has always been a hub of Islamic learning. Scholars from far and wide come to study here, continuing a tradition that goes back to the Prophet Muhammad (Peace be upon him) himself. Madinah’s universities and religious institutions play a key role in preserving and spreading Islamic knowledge.
Madinah in the Present
Today, Madinah is a modern city within Saudi Arabia. It balances centuries-old traditions with the needs of today’s pilgrims. Here’s what that looks like:
- Managing Growth: The Saudi government works tirelessly to expand Madinah’s infrastructure to accommodate millions of visitors each year. This includes new hotels, transportation systems, and renovations of the holy sites.
- Serving Pilgrims: Medina’s economy focuses on serving pilgrims. People work in hotels, restaurants, transportation, and shops that cater to the specific needs of visitors.
- Global Symbol: Madinah remains a powerful symbol of faith for Muslims worldwide, a reminder of where our religion began and a source of spiritual inspiration.
The Everlasting Light
While Madinah has grown and changed, its essence remains. It’s a place where the legacy of the Prophet Muhammad (Peace be upon him) lives in the hearts of Muslims across the world. The city stands as a testament to the power of faith, the importance of community, and the enduring message of Islam.
Conclusion
From its beginnings as Yathrib to the Radiant City, it is today, Madinah holds a special place in every Muslim’s heart.
This city witnessed the Prophet Muhammad’s (Peace be upon him) triumphs and challenges, and it’s where the principles of Islam took root and spread throughout the world.
Whether you experience Madinah’s bustling streets and economy centered around serving pilgrims, praying in its historic mosques, or learning about its history, Madinah’s message is clear: peace, compassion, and unwavering faith in Allah.
Even with challenges like the ad dajjal neither plague, Madinah reminds us that the light of Islam will always endure.
Thank you for journeying with me through Madinah. I hope it has deepened your understanding and appreciation of this extraordinary city!
Frequently Asked Questions
Can non-Muslims visit Madinah?
Unfortunately, the holy city of Madinah is closed to non-Muslims. It’s a sacred place within Islam and entry is restricted in order to preserve its religious significance.
What is the best time of year to visit Madinah?
Madinah can get very hot, so avoid peak summer months. Consider visiting during spring or fall, or during Ramadan for a spiritually charged atmosphere (but be prepared for larger crowds).
How can I get to Madinah?
Madinah has an international airport (Prince Mohammad bin Abdulaziz International Airport) with flights from many countries. You can also travel overland from other cities within Saudi Arabia.
Is Madinah safe to visit?
Madinah is considered a safe city for pilgrims and generally has low crime rates. Always be mindful of your belongings and surroundings, especially in crowded areas.
What are the must-see places in Madinah?
Masjid al-Nabawi (the Prophet’s Mosque), Al-Baqi Cemetery, Quba Mosque, and Mount Uhud are essential sites. You might also be interested in the Seven Mosques or exploring Madinah’s museums.

